Essential Guide to Avoid Brain-Eating Amoeba: Stay Safe in 2025
As we step into 2025, awareness of health risks associated with water safety is more crucial than ever. The brain-eating amoeba, scientifically known as Naegleria fowleri, is a rare but devastating pathogen that can lead to severe neurological consequences if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding how to prevent an infection and recognizing safe swimming practices can significantly reduce the risk of encountering this dangerous organism.
In this guide, we will explore the ways to avoid brain-eating amoeba, focusing on key prevention strategies, the importance of maintaining hygiene, and the necessary awareness surrounding recreational water safety. With basic knowledge, the dangers of Naegleria fowleri can be mitigated effectively, ensuring a safer environment for everyone.
Key topics include the symptoms of amoeba infection, safe practices for swimming in freshwater, and health education initiatives designed to inform the public. Through conscientious efforts, we can build a resilient community equipped with the knowledge necessary for protecting our neurological health.
Understanding the Risks of Naegleria Fowleri
Building on the significance of water safety, it is essential to understand the risks associated with Naegleria fowleri. This amoeba thrives in warm freshwater environments, such as lakes, hot springs, and poorly maintained swimming pools. To stay safe, it’s critical to recognize the circumstances under which infections occur.
What is Naegleria Fowleri?
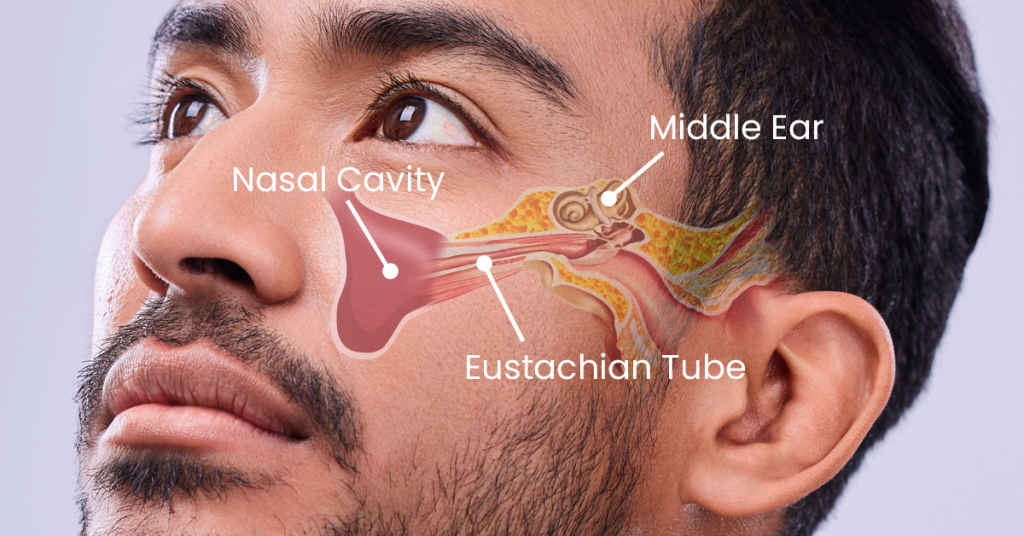
Naegleria fowleri is a heat-loving amoeba found in freshwater and is known to cause amoebic meningoencephalitis, a severe brain infection. Although infections are rare, they are often fatal, occurring when the amoeba enters the body through the nose, typically during swimming or diving in warm freshwater.
This highlights the importance of educating swimmers on safe water practices and making informed choices about water activities. The risk of infection increases in warm conditions, particularly when water temperatures exceed 30°C (86°F).
Symptoms of Amoeba Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of an amoeba infection is vital for early detection. Initial symptoms include severe headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, and a stiff neck. As the infection progresses, neurological symptoms such as seizures and altered mental status may occur.
Timely identification and treatment can greatly improve outcomes, making it essential for individuals engaging in freshwater activities to be aware of these warning signs.
Health Risks Associated with Infections
Infections caused by Naegleria fowleri can have devastating health effects. The progression of amoebic meningoencephalitis often leads to severe neurological impairment or death. Understanding these risks can motivate individuals to adopt safer swimming practices and advocate for community health measures, such as monitoring water quality.
Preventing Infection Through Safe Swimming Practices
To mitigate the risks associated with Naegleria fowleri, adopting safe swimming practices is essential. Following guidelines and health education initiatives can play a significant role in protecting individuals and communities from infection.
Safe Swimming Guidelines
A key component of preventing amoeba infection is adhering to established swimming safety guidelines. This includes choosing swimming locations wisely, primarily chlorinated pools, which significantly reduce the risk of exposure to Naegleria.
Additionally, swimmers should avoid underwater diving in warm freshwater and refrain from splashing water that could enter the nose. Opting for chlorinated facilities, which are rigorously maintained, can help ensure safer recreational experiences.
Proper Water Handling Techniques
Practicing proper water handling techniques is crucial in everyday situations. For example, when using neti pots or similar devices, always use distilled, sterile, or previously boiled water to avoid potential exposure to harmful pathogens. Guidelines for maintaining hygiene must be followed diligently to minimize the chances of infection.
Monitoring water quality and using safe water sources can also contribute to effective prevention strategies. Make a habit of checking local health department reports on water quality and any advisories regarding recreational water use.
Awareness and Education Programs
Promoting public awareness about the health risks associated with Naegleria fowleri is vital. Community health programs can strengthen collective knowledge and foster safer water practices. Implementing educational workshops, informative campaigns, and outreach initiatives can empower individuals with the knowledge needed to protect themselves.

Maintaining Hygiene and Early Detection of Symptoms
With the focus on prevention strategies, maintaining hygiene forms a foundational element in protecting individuals from Naegleria fowleri. Attention to personal hygiene can significantly reduce exposure to waterborne pathogens in recreational settings.
Importance of Personal Hygiene for Swimmers
Swimmers should adopt meticulous hygiene practices, such as showering before entering pools or natural water bodies. This not only elevates personal cleanliness but also helps maintain the cleanliness of communal and public waters.
Recognizing the importance of proper hygiene habits among families is fundamental. Through education and positive reinforcement, children can learn the significance of washing hands and understanding the potential risks associated with contaminated water.
Early Detection and Treatment Options
If symptoms are detected early, prompt medical intervention can substantially improve health outcomes. Seek medical help immediately if any signs of infection appear following exposure to warm freshwater environments. Treatments may vary, including antifungal medications and supportive care.
Monitoring for symptoms is particularly important for individuals engaging in high-risk water activities. Make it a point to stay informed about potential health warning signs and prioritize timely consultation with healthcare professionals.
Community Role in Water Safety Awareness
As we consider personal safety, community involvement in promoting water safety awareness is crucial. Collective education, health campaigns, and community health measures can significantly reduce the public risk of Naegleria fowleri and other waterborne illnesses.
Collaborative Efforts for Health Education
Communities can thrive through partnerships focused on health education and safety. By collaborating with local health departments, schools, and recreational facilities, essential information regarding safe swimming practices and prevention strategies can be disseminated effectively.
Community workshops and outreach programs can facilitate the sharing of valuable information, further enhancing public awareness and encouraging responsible behaviors related to water activities.
Monitoring Water Quality and Environmental Factors
Environmental health plays a crucial role in preventing infections. Monitoring water quality regularly helps identify potential hazards, thus promoting safer swimming environments. Communities must advocate for sustainable practices and protect freshwater resources through engagement with local health regulations.
As we approach summer, being aware of the climatic impact on water safety will also underscore the importance of vigilance in recreational water use. Regular assessments and proactive measures contribute to creating reliable and safe water sources.
Engaging Families in Safety Practices
Family participation in water safety education helps instill responsible habits among younger members. Teaching children about the risks of warm freshwater swimming and the importance of hygiene can create a lasting foundation for future generations.
Effective communication strategies can ensure that families remain aware of safety guidelines, ultimately enhancing community expectations around recreational water activities.
``` Its part of generated content. Can i generate another part?