“`html
Essential Guide to Finding the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
In the world of geometry, understanding the **surface area of rectangular prisms** is crucial. Whether for academic purposes or practical applications, knowing how to **calculate surface area** can greatly enhance your comprehension of **3D shapes**. In this guide, we will explore various methods and techniques to accurately find the surface area, delve into related concepts such as **volume of rectangular prisms**, and familiarize ourselves with **rectangular prism dimensions**. Let’s get started!
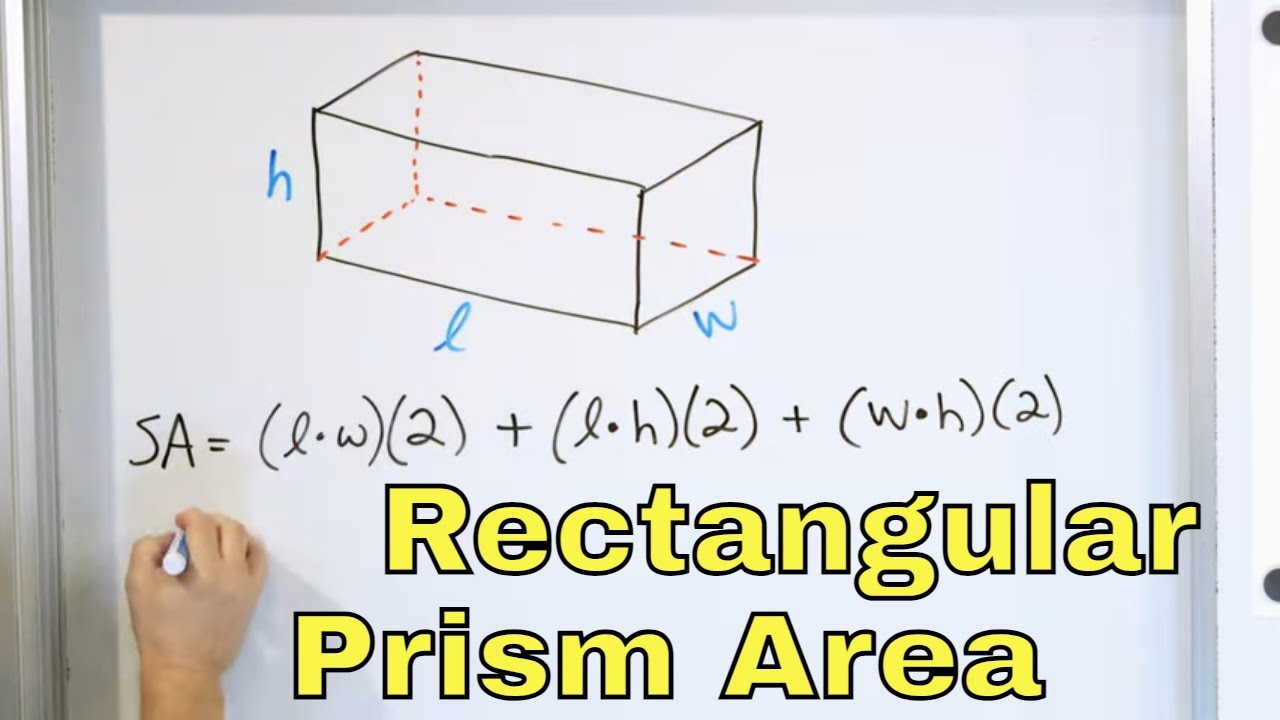
Understanding the Surface Area Formula
The **surface area formula** for a rectangular prism is essential for anyone looking to grasp the basic geometry principles behind three-dimensional objects. To determine the total surface area, you need to know the dimensions: **length, width**, and **height**. The formula is simplified as:
**Surface Area = 2(lw + lh + wh)**
Using this formula allows for easy **area calculations** for each of the faces of the prism, summing them up to get the total surface area. Each of the three dimensions contributes differently based on its position in the formula, emphasizing the important relationship between these measurements when calculating the **surface area of a rectangular prism**.
Breaking Down the Surface Area Calculation
When calculating the surface area, the first step involves identifying the **length, width, and height** of the prism. Each rectangular face of a prism can be calculated individually, which facilitates an easier understanding of the **area of faces**. For instance, consider a prism with:
- Length: 5 cm
- Width: 3 cm
- Height: 4 cm
Having established the dimensions, you can compute the area of each pair of rectangular faces:
- Top and bottom faces: 2(lw) = 2(5 cm * 3 cm) = 30 cm²
- Front and back faces: 2(lh) = 2(5 cm * 4 cm) = 40 cm²
- Left and right faces: 2(wh) = 2(3 cm * 4 cm) = 24 cm²
Summing these areas gives you a total surface area of 94 cm² for this specific prism.
Practical Application of Surface Area
Understanding how to find the **surface area of a rectangular prism** has numerous practical implications. For instance, in fields such as construction and packaging, calculating the surface area is pertinent for estimating the amount of material required. In geometry, this can translate to lessons about **area measurement strategies** and real-world applications. A constructor needs to calculate the surface area before applying paint or installing insulation, indicating a direct link between geometric principles and daily tasks.
Geometric Shapes and Volume Calculations
In addition to surface area, the concept of **volume of rectangular prisms** plays a significant role in mathematical comprehension. The volume gives insight into the space a prism occupies. The formula used to calculate the volume is significantly straightforward:
**Volume = length × width × height**
This formula not only complements the surface area formula but also reinforces the understanding of three-dimensional geometric shapes. By integrating both formulas into your methods for **area calculations for construction**, you gain a holistic view of spatial measurements.
Real-Life Examples in Surface Area Calculation
To solidify comprehension, consider a real-life example. If you have a storage box in the shape of a rectangular prism with a length of 12 ft, width of 5 ft, and height of 3 ft, using the surface area formula would look like this:
- Surface Area = 2(12*5 + 12*3 + 5*3)
- Surface Area = 2(60 + 36 + 15) = 222 ft²
This calculation assists in determining how much wrapping paper you’d need for a gift box, showcasing the **practical applications of surface area** in everyday scenarios.
Comparing Area and Volume Differences
When discussing areas and volumes together, it’s essential to understand how these two concepts differ. The **area of rectangles** helps determine the amount of two-dimensional space covered by a prism, while the volume tells us how much three-dimensional space the object occupies. This distinction is valuable for **geometry education**, where students learn to differentiate between various measurements and what they represent.
Unit Conversion and Measuring Techniques
Accurate measurement is vital when dealing with real-world dimensions. **Unit conversion** is often necessary when you’re working in different measurement systems, such as converting inches to centimeters. A solid understanding of how to measure various dimensions correctly enhances the accuracy of your calculations. Worksheets and practice problems in **surface measurement technique** can greatly assist learners in practicing these skills.
Visual Aids for Understanding Surface Area
Using **surface area visual aids**, like diagrams, can deepen comprehension of theoretical concepts. Tools such as 3D models or interactive online resources help visualize the relationship between the various dimensions of a prism. For example, neat, labeled diagrams highlighting the length, width, and height can make it easier to grasp dimensional concepts. This is especially useful in **geometry homework help**, where visual learning supports complex calculations.
Hands-On Geometry Activities
Engaging with geometry in tangible ways through **hands-on activities in geometry** reinforces learning. Building small scale physical models of rectangular prisms using cardboard or clay not only makes learning fun but solidifies students’ understanding of both **volume calculations** and surface area. By manipulating real-world materials, students can apply mathematical formulas in practice, reinforcing insight into the **rectangular prism properties**.
Key Takeaways
- The **surface area formula** for a rectangular prism is rooted in the dimensions: length, width, and height.
- Recognizing the difference between **area of faces** and **volume of rectangular prisms** is essential in geometry.
- Unit conversion and measuring techniques significantly impact the accuracy of calculations.
- Hands-on activities and visual aids can support effective learning and understanding of geometric properties.
FAQ
1. What is the formula to find the volume of a rectangular prism?
The formula to calculate the volume of a rectangular prism is straightforward: **Volume = length × width × height**. This calculation gives you the total space inside the prism, supporting a better understanding of **spatial reasoning**.
2. How does unit conversion affect surface area calculations?
Unit conversion can significantly alter the accuracy of your **surface area calculations**. When dimensions are converted from one unit to another, ensure that all measurements are in the same unit to attain a correct area. This principle is crucial in **dimensional analysis**, where consistent measurements yield valid results.
3. Why is understanding volume important in geometry?
Understanding volume provides insight into how much space a three-dimensional object occupies, which is directly linked to many practical applications like storage and capacity planning. Furthermore, it complements **area calculation** as students explore the relation between two and three-dimensional shapes.
4. What practical applications use the concept of surface area?
Surface area is vital in various fields, such as packaging, painting, and insulation. Knowing how much surface area an object has helps in calculating material amounts or costs effectively, demonstrating the **practical applications of surface area** in real life.
5. Can you provide an example of a rectangular prism calculation?
Sure! For example, if you have a rectangular prism with dimensions of 8 inches (length), 4 inches (width), and 5 inches (height), the surface area will be calculated as follows:
**Surface Area = 2(8*4 + 8*5 + 4*5) = 2(32 + 40 + 20) = 264 in²**. This helps highlight the entire exterior surface, showcasing how surface area can be effectively calculated through consistent formulas.
“`