“`html
Top 5 Effective Ways to Minimize Your Flu Risk After Exposure
Understanding Flu Exposure Time and Risks
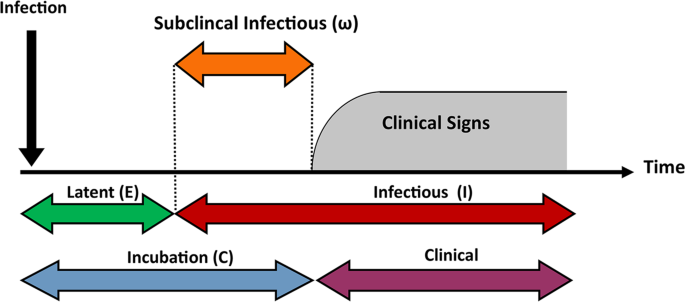
When it comes to **flu symptoms** and determining the right response after potential exposure, understanding the **flu exposure time** is critical. The **influenza incubation period**, which typically ranges from one to four days, indicates how long it may take for symptoms to appear after exposure. Knowing the **flu contagious period** can further help individuals understand their risk and the best preventive measures. For instance, if you were in contact with someone presenting **early flu symptoms**, it’s advisable to monitor yourself for up to a week. Incorporating good hygiene practices such as frequent hand washing and using hand sanitizers can effectively reduce your risk, especially during heightened **flu season**.
Flu Infection Timeline: Key Markers to Watch
Monitoring the **flu infection timeline** is essential in identifying the onset of the illness. Symptoms typically develop anywhere from 1 to 4 days after exposure, as indicated by research on **flu transmission timing**. You might start experiencing **flu symptoms** like fever, muscle aches, and fatigue. Understanding how long the flu takes to show up helps in tracking any potential infection early. If within this timeframe, you notice more persistent symptoms, it may be important to alert your healthcare provider for appropriate treatment options. Early detection can significantly affect the severity of the illness and its **flu complications**.
Flu Contagiousness: How Long is the Risk?
Knowing how long the **flu is contagious** is vital for anyone who might have been exposed. Generally, an individual infected with the flu virus is contagious the day before symptoms appear and can continue to spread the virus up to a week after falling ill. This **flu contagiousness** emphasizes the importance of staying away from others if you develop symptoms, even mild ones. Taking proactive measures, such as wearing masks and frequent sanitization of surfaces, can help contain the virus, minimizing overall exposure.
Effective Flu Prevention Methods
Once you understand flu exposure and its risks, the next step is to implement effective **flu prevention methods**. The most proactive approach is scheduling your **flu vaccination**. Vaccination helps bolster your immune system against seasonal flu strains that are prevalent that year. It’s recommended to get vaccinated well in advance of **flu season** as it takes about two weeks for the body to develop protection. Regularly reviewing **flu vaccination benefits** and considering timely shots each year can pave the way for a healthier future.
Healthcare and Community Responses to Flu Transmission
Another critical piece of **flu prevention** is understanding **flu transmission dynamics** within the community. Engaging in local health awareness initiatives and campaigns can boost knowledge of how the flu spreads. For instance, during outbreaks, health departments typically offer guidelines and responses strategies. They often provide insights into safe practices such as avoiding crowded places and maintaining social distance wherever possible, especially amidst ongoing flu outbreaks. Staying informed and participating in community health initiatives can substantially reduce flu transmission rates.
Personal Health Management Strategies
Personal health management plays a significant role in reducing exposure. Emphasizing *health education*, particularly for high-risk groups (like seniors and those with chronic conditions), can make a notable difference. Simple actions such as maintaining good nutrition and hydration, getting enough sleep, and exercise can enhance your immune response against infections. Furthermore, consulting on **flu management strategies** can bolster one’s health literacy, which is crucial during **flu season** when the risks are heightened.
Flu Treatment Options and Recovery
If exposure to the flu has occurred, understanding your treatment options is essential for recovery. If you start noticing typical **flu symptoms**, seeking early medical advice will be beneficial. **Flu treatment options** include antiviral medications that can shorten the duration of the illness when taken soon after symptoms begin. In addition to antiviral therapies, **flu care guidelines** encourage symptomatic treatment such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications for pain relief and fever reduction. This overview post-exposure can drastically decrease recovery time and help you return to health more rapidly.
Flu Recovery Time: What to Expect
The **flu recovery time** generally varies depending on overall health and the timing of treatment. Most individuals typically recover within a week or two, but ongoing vigilance in tracking your symptoms is recommended, particularly for potential **flu complications**. Attentively observing your body’s responses and scheduling follow-up visits with your healthcare provider can contribute to a more seamless recovery.
Handling Flu Challenges and Finding Resources
Lastly, there may be challenges regarding the **flu** that arise from misinformation and low awareness. Taking the initiative to educate yourself through reliable resources is crucial. Understanding the nuances of **flu symptoms** versus common cold can also lead to better decision-making in case of illness. Stay informed about local health department guidance and relevant healthcare communications to maximize your knowledge when managing flu risks.
Key Takeaways
- Monitor flu exposure timings and symptoms closely for effective early action.
- Utilize flu vaccines as a key strategy for flu prevention.
- Engage with community health initiatives to improve flu awareness and control.
- Seek timely treatment options to minimize flu symptoms and ensure proper recovery.
- Invest in personal health management to reduce the risk of flu infection.
FAQ
1. How does flu spread through communities?
The flu typically spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Maintaining distance and practicing good hygiene can help reduce transmission risks in community settings.
2. What are the early signs of flu infection?
Early signs can include fever, chills, muscle aches, fatigue, cough, runny nose, sore throat, and headaches. Recognizing these **early flu symptoms** is vital for prompt medical care.
3. What preventive measures should I take during flu season?
Staying healthy during flu season includes getting vaccinated, frequent hand washing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and practicing good respiratory hygiene.
4. Are antiviral medications effective for existing flu infections?
Yes, antiviral medications can lessen symptom severity and duration when they are started within the first few days of illness, playing a crucial role in **flu treatment options**.
5. How long does the flu virus survive on surfaces?
The flu virus can survive on hard surfaces for 24 hours and on fabrics for several hours. Regular sanitation of commonly touched surfaces can help prevent flu spread.
“`