Effective Ways to Calculate Percent Yield
Understanding the Percent Yield Formula
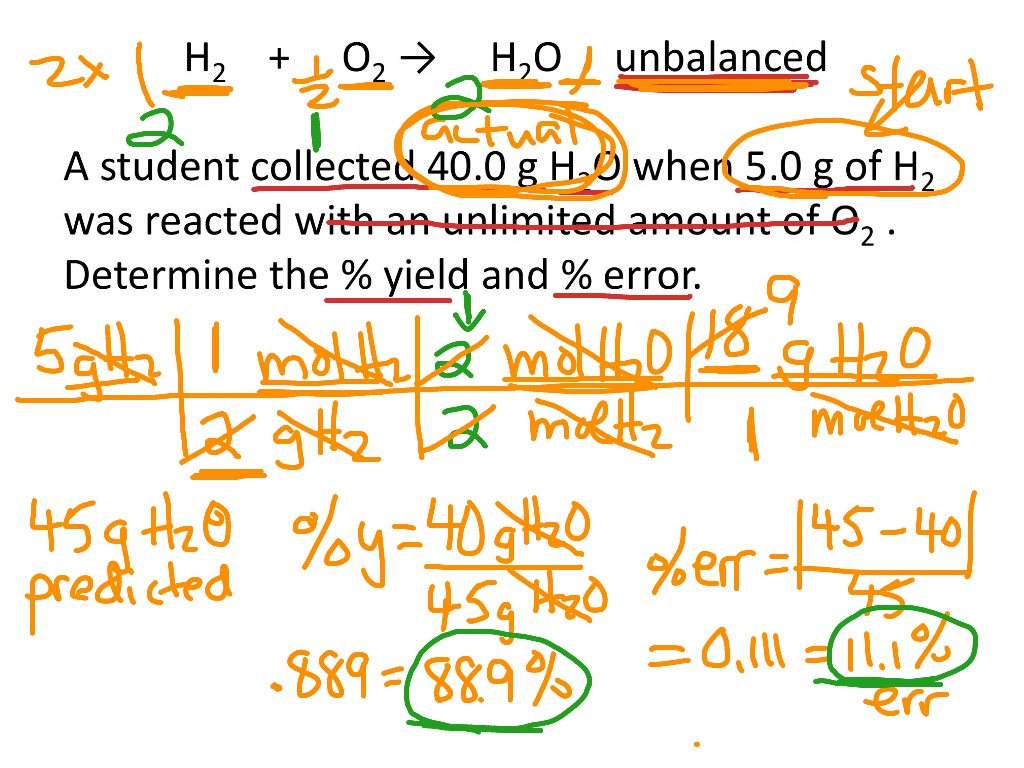
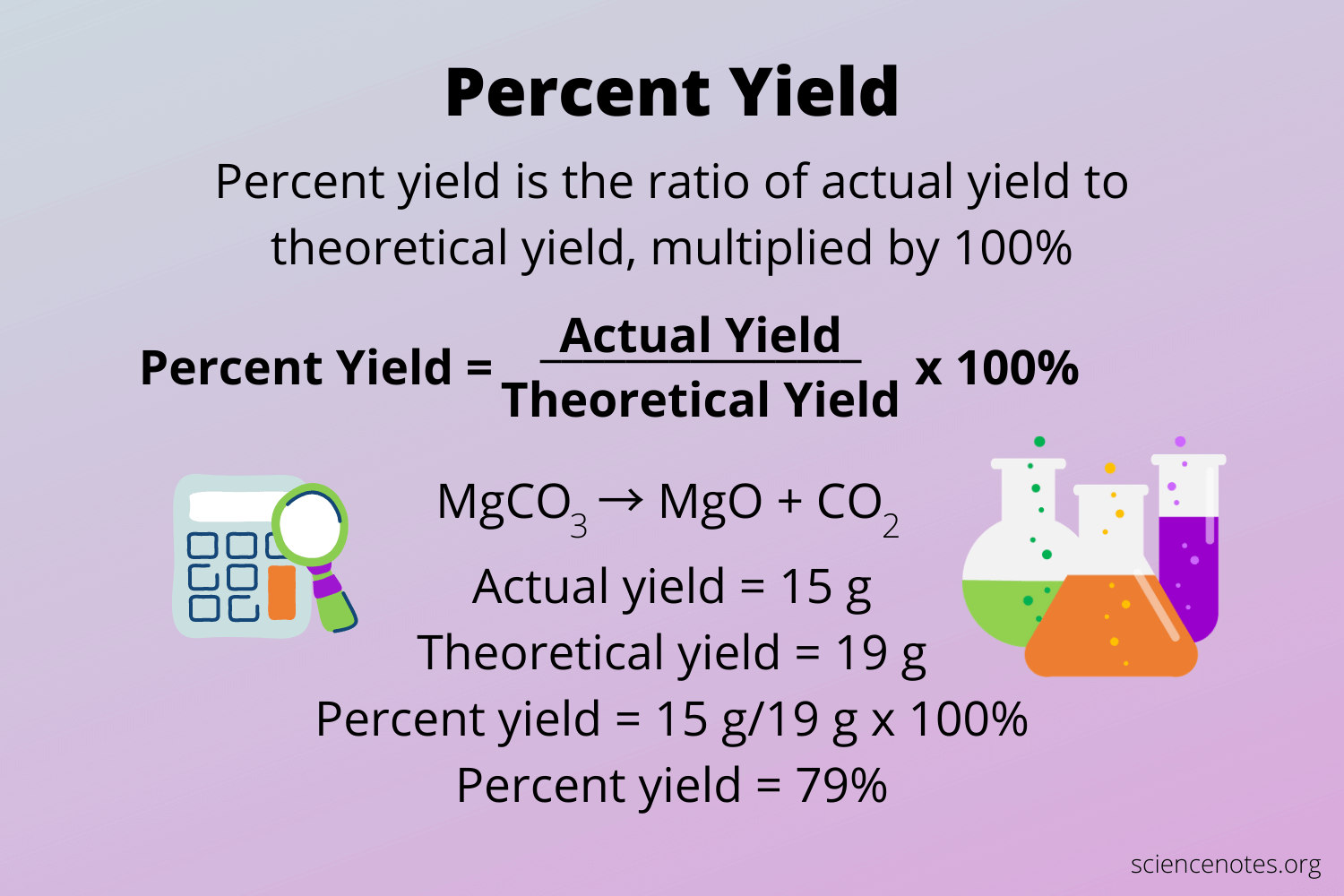
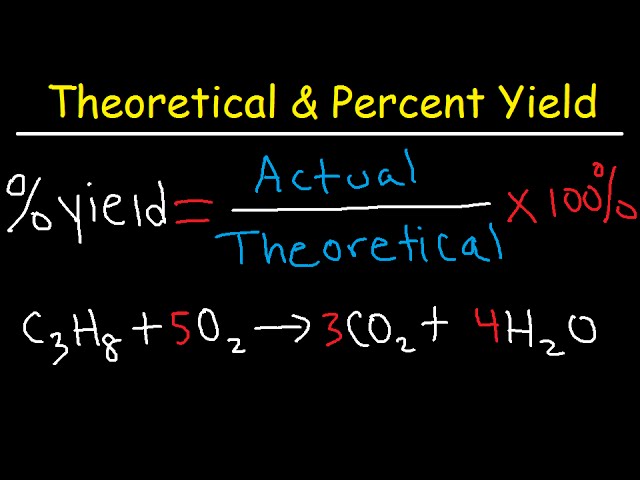
The **percent yield** is a crucial metric in chemistry, used to evaluate the efficiency of a chemical reaction. It compares the actual yield of a product obtained from a reaction to the theoretical yield, which is the maximum amount that could be produced based on stoichiometric calculations. The **percent yield formula** is given as: Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100. This formula is vital for chemists as it helps them determine how effectively a reaction produces its desired outcome. In practical applications, understanding this formula enables scientists to analyze the efficiency of their chemical reactions and improve their processes intelligently.
Breaking Down the Yield Calculation
To calculate percent yield accurately, one must first identify the **theoretical yield**, which can often be computed using stoichiometric relationships established from balanced chemical equations. For instance, if a reaction is expected to produce 50 grams of a compound but you only get 40 grams, the **actual yield** is 40 grams. Applying the formula mentioned earlier, we can calculate the percent yield: Percent Yield = (40 grams / 50 grams) × 100 = 80%. This percentage offers insight into how successful a chemical reaction was, highlighting the importance of determining percent yield in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Example of Percent Yield Calculation
Let’s take a practical example to observe how **percent yield calculation** works in a laboratory setting. Suppose you are experimenting with the synthesis of water from hydrogen and oxygen gases: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O. If theoretically, 100 grams of water can be created, but your experiment yields only 85 grams, you would calculate your percent yield as follows: Percent Yield = (85 grams / 100 grams) × 100 = 85%. This calculation indicates a relatively efficient synthesis process. Such yield assessments are critical for developing potent laboratory techniques and optimizing operations.
Factors Affecting Percent Yield
Various factors can influence percent yield in chemical reactions, leading to disparities between actual and theoretical yields. Understanding these factors plays a vital role in maximizing percent yield. Some key elements include the purity of reactants, reaction conditions, and experimental techniques. Impurities in the starting materials can lead to unwanted side reactions, which may reduce the quantity of the intended product and thus impact the **yield percentage**. Additionally, fluctuations in temperature and pressure can alter the reaction kinetics, reducing the reaction’s effectiveness.
Techniques to Improve Yield Efficiency
To achieve the highest percent yield, chemists employ several strategies to enhance reaction conditions. For instance, optimizing temperature and concentration can significantly affect reaction rates and efficiencies, enabling greater product recovery. Using catalysts can also improve reaction outcomes by lowering the energy barrier needed for reactions to proceed, further enhancing the **chemical yield**. By keeping meticulous records of the actual yield alongside theoretical predictions, chemists can analyze experimental results and refine their protocols to minimize waste and maximize production.
The Role of Stoichiometry in Percent Yield
The relationship between reactants and products in **stoichiometry** greatly influences the **percent yield in experiments**. Skilfully balancing equations ensures that chemists accurately predict theoretical yields, which is fundamental in guiding their yield analysis. Moreover, understanding stoichiometry helps identify limiting reactants which can dictate the maximum amount of product formed during a reaction. This knowledge enables researchers to tailor conditions and optimize processes, leading to improved yield assessment and a greater understanding of reaction dynamics.
Practical Applications of Percent Yield in Chemistry
Percent yield calculation is not only theoretical; it has significant practical implications in chemical production and laboratory environments. Industries rely heavily on yield maximization to optimize resource use and increase profitability. For example, in pharmaceutical production, achieving high percent yield directly correlates with reduced costs and efficient use of raw materials. It also minimizes waste, contributing to more sustainable practices in chemical manufacturing.
Yield Loss Analysis in Chemical Reactions
Analyzing potential yield loss is an essential aspect of **yield optimization**. In any reaction, several points can lead to loss, such as incomplete reactions, by-product formation, or even losses during purification processes. By evaluating potential causes of yield loss and implementing measures to reduce these factors, researchers can significantly enhance the final product yield. For example, performing purification steps in a closed system can help minimize losses due to evaporation or adherence to equipment surfaces.
Importance of Accurate Yield Calculation
Accurate yield calculation cannot be overstressed, especially in large-scale chemical processes where even small improvements can lead to substantial financial savings. Practices such as regular calibration of measuring instruments, maintaining precise laboratory conditions, and retraining staff can all contribute to more reliable yield assessments. Moreover, employing statistical tools in the yield calculation can further bolster accuracy and help identify trends over time, making yield analysis more robust and informative.
Summary and Key Takeaways
- The **percent yield formula** is a pivotal equation in determining the efficiency of chemical reactions.
- Real-world applications of yield calculations serve to optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance profitability.
- Understanding and improving factors affecting yield can lead to better research outcomes and more efficient laboratories.
FAQ
1. What is percent yield in chemistry?
**Percent yield** in chemistry is a ratio showing how much product was obtained from a chemical reaction compared to the maximum theoretically possible yield. It is expressed as a percentage and calculated using: (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100. Understanding percent yield helps chemists assess the effectiveness and efficiency of their reactions.
2. How can I maximize the percent yield in an experiment?
To maximize the **percent yield** in an experiment, ensure optimal reaction conditions such as temperature and concentration. Use catalysts to increase reaction rates and adhere to proper stoichiometric ratios. Additionally, surprise variable monitoring and minimizing potential yield losses through careful experimental design can significantly aid in achieving higher yields.
3. What does a low percent yield indicate?
A low **percent yield** indicates inefficiency in a chemical reaction, suggesting potential issues such as incomplete reactions, zero mass transfer, or by-product formation. Analyzing these outcomes can lead to improvements in experimental techniques and chemical process design to achieve more effective reactions in the future.
4. What are common exercises to calculate percent yield?
Common exercises in calculating percent yield include using balanced chemical equations to find theoretical yields, conducting experiments to acquire actual yields, and practicing with various substances to reinforce the importance of stoichiometry in yield calculations. Understanding these core concepts is key to effective **yield analysis**.
5. How does understanding yield assist in resource management?
Understanding yield is essential for **resource optimization**. High efficiency in producing desired products leads to less waste and reduced resource usage, promoting more sustainable practices in chemical production. Moreover, accurate yield calculations can enhance economic outcomes, resulting in better management of both funds and materials.