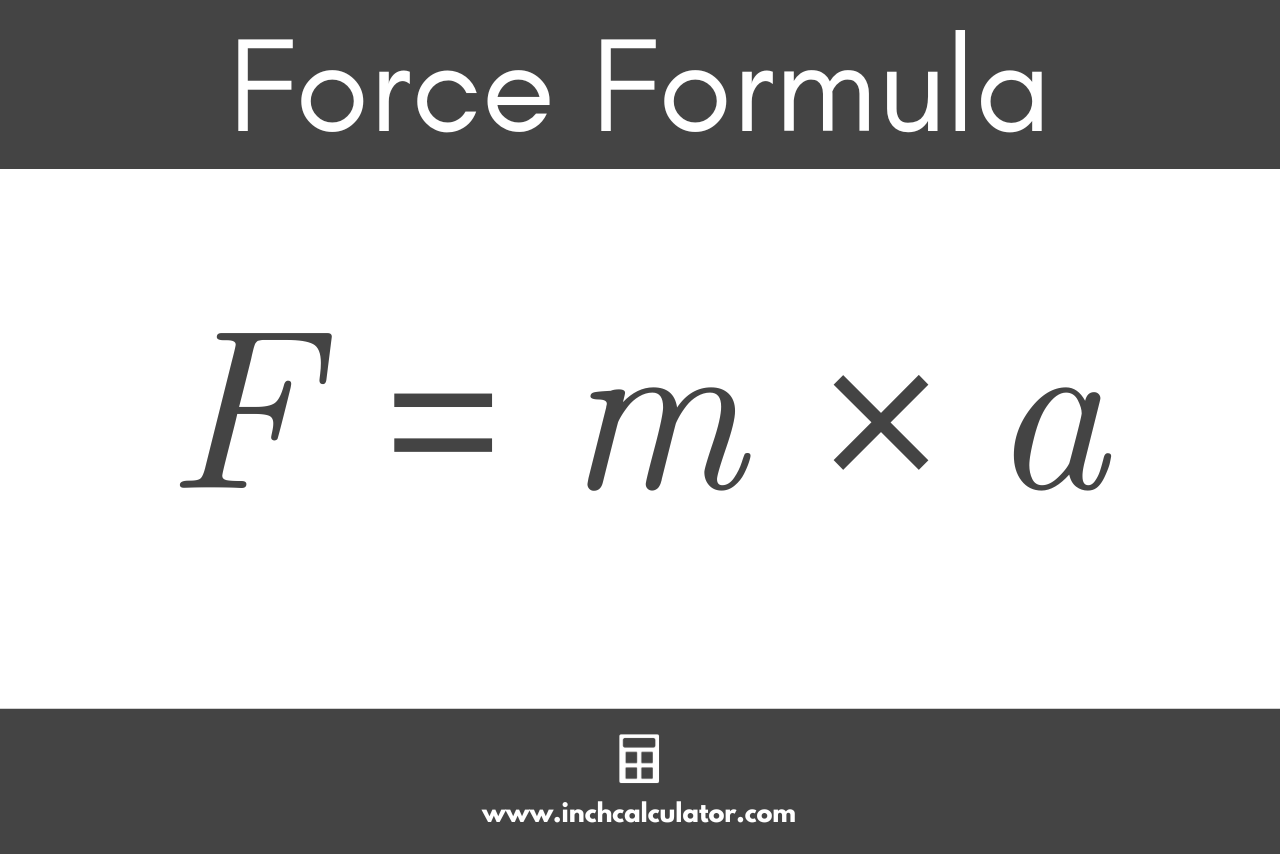“`html
How to Properly Calculate Force: Effective Methods for Physics and Engineering in 2025
Understanding the Basics of Force Calculation
To effectively calculate force, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles involved in physics. The foundational basis of force is captured in Newton’s second law, which states that the net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object multiplied by its acceleration. This is mathematically represented as: F = m × a, where F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration. Familiarity with this equation allows technicians and engineers to understand how force in physics plays a role in mechanical systems, safety designs, and everyday activities.
The Importance of Force Units in Calculations
When discussing force units, the most commonly used unit is the Newton (N), defined as the force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass by one meter per second squared. Understanding these units is crucial for accurately performing force calculations across different scenarios. Additionally, other units may be relevant depending on the country or context, and converting between these measurements can be an important step in force measurement. For example, while engineers may often work in Newtons, it’s important to recognize that in some fields or regions, other units like pounds or dynes might be prevalent.
Force Calculation Formula and Application Examples
Utilizing the force calculation formula, numerous examples can be illustrated across various disciplines. For example, in engineering, to determine the force exerted by a structure under load, an engineer could evaluate the mass of the materials and the acceleration due to gravity. Furthermore, other types of forces, such as gravitational force, frictional force, and even dynamic forces, can be calculated using tailored equations.
Types of Forces and Their Applications
Understanding the various types of forces is vital for analyzing scenarios involving physics and engineering. These forces can be classified broadly into two categories: contact forces and non-contact forces. Contact forces, such as friction and tension, occur when objects physically interact, whereas non-contact forces like gravitational force and magnetic force act across distances. Being able to categorize force types aids in predicting outcomes in force problems and scenarios.
Exploring Net Force and Resultant Force
One of the key concepts in force analysis is determining the net force. The net force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object. Whether forces are balanced or unbalanced, understanding the net force is critical in defining how an object will move. For example, if two people are pushing against each other with equal strength, the forces are balanced, resulting in no movement. Conversely, if one person exerts a greater force, the object moves in that direction, illustrating the principles of unbalanced forces.
Force Diagrams: Visualizing Forces
The use of force diagrams plays a significant role in force analysis. These diagrams allow for visual representation of all forces acting on an object, making it easier to compute the net force. By indicating direction and magnitude, engineers and students can better visualize interactions and make accurate calculations. For instance, in a problem assessing the frictional forces on a moving object, a force diagram can greatly simplify the summation process necessary to calculate the resultant force acting on the object.
Practical Applications of Forces in Everyday Life
Recognizing the impacts of force in engineering and everyday situations allows individuals to appreciate the ubiquitous nature of force. Forces are involved in biomechanics like walking, driving, or any form of motion. Engaging with force examples in real life helps ground theoretical knowledge into practical applications. From determining the force needed to lift an object using a lever to understanding how acceleration affects a vehicle’s motion, these principles are continuously at play.
Analyzing Everyday Force Scenarios
Analyzing everyday force scenarios provides educational insight into physics concepts. For instance, when attempting to push a heavy box across a room, one must account for both the applied force and the opposing frictional force. By applying the principles of force calculations, one can determine if enough applied force is present to overcome friction and achieve movement. This hands-on approach solidifies the understanding of force applications and laws.
Innovations in Force Measurement Techniques
With advancements in technology, measuring force has become increasingly sophisticated. New methods and sensors allow for precise force measurement, in contexts such as sports, where monitoring the forces a player applies can lead to performance improvements. Engineers also explore advanced systems that use algorithms for real-time analysis of forces, providing a better grasp of dynamic forces in various conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Newton’s second law provides the foundation for understanding force calculation.
- Identifying types of forces allows for better application in real-world scenarios.
- Force diagrams facilitate the analysis of net forces and resultant forces.
- The study and measurement of forces are crucial in both physics and engineering disciplines.
- Practical applications of force concepts enhance understanding and problem-solving skills.
FAQ
1. What is the best method to calculate gravitational force?
Gravitational force can be calculated using the formula F = G(m1 × m2) / r², where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between their centers. This equation emphasizes the relationship between the masses and the distance, critical for understanding gravitational interactions.
2. How can I visually represent forces acting on an object?
A force diagram, or free-body diagram, can be created to visually represent the forces acting on an object. This method includes arrows indicating the magnitude and direction of each force, helping to simplify force calculations and determine net forces effectively.
3. What are common types of frictional forces?
Common types of frictional forces include static friction, which prevents movement between resting surfaces, and kinetic friction, which occurs between moving surfaces. Understanding these frictional forces is crucial in applications like engineering, where they impact the motion of machinery and vehicles.
4. What role do forces play in sports dynamics?
In sports, forces significantly influence performance, techniques, and safety. For example, understanding the forces during a basketball shot involves analyzing the applied force, gravitational pull, and friction from the surface. This knowledge helps coaches and athletes optimize performance.
5. How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect motion?
Balanced forces lead to an object remaining at rest or continuing at a constant velocity, while unbalanced forces cause an object to accelerate or change direction. Thus, understanding these concepts is critical in predicting and analyzing motion in different contexts, including engineering applications.
“`