Effective Ways to Find the Volume of a Triangular Prism
Understanding the Triangular Prism Volume Formula
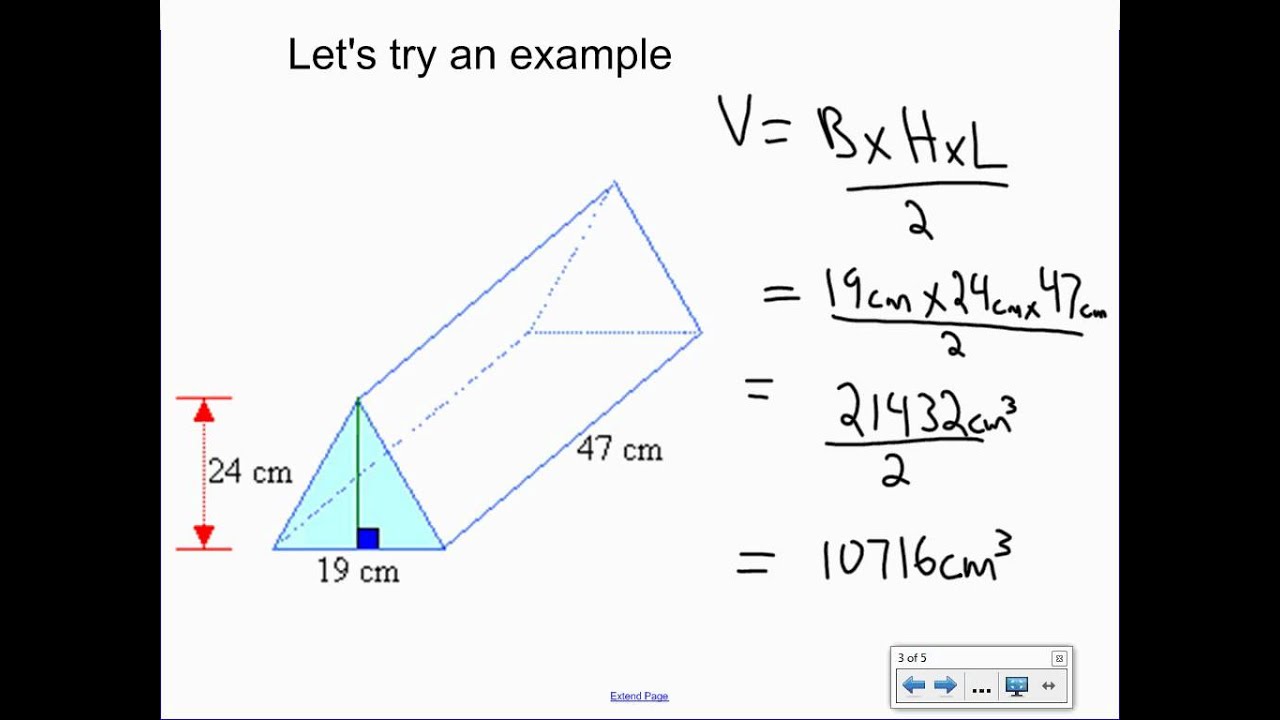
The **volume of a triangular prism** is a crucial concept in geometry, especially in understanding solid shapes like prisms. To calculate this volume, we can apply a specific **triangular prism formula**. This formula revolves around two primary factors: the area of the base triangle and the height of the prism. The basic formula can be expressed as:
Volume = Base Area × Height
To effectively utilize this equation, first, determine the **base area of the triangular prism** by employing the **triangular area formula**. Understanding the **height of the triangular prism** is equally important, as it directly influences the total volume. These concepts play an important role in various geometric applications and are foundational to many advanced math topics encountered in education.
Calculating the Base Area of the Triangular Prism
The **base area of a triangular prism** can be found using the **formula for area of a triangle**, which is crucial for the initial step in finding volume. The formula is expressed as:
Base Area = 0.5 × Base × Height of the triangle
To apply this formula, you need measurements of the base’s length and the height of the triangle itself. For instance, if the base of the triangle measures 6 cm and the height of the triangle is 4 cm, the base area would be:
Base Area = 0.5 × 6 cm × 4 cm = 12 cm²
This calculation is pivotal, as it sets the stage for incorporating the height of the **triangular prism** into our volume calculation. Remember, accurate measurements and calculations lead to correct results in potential volume requirements.
Key Volume Calculation Steps
Once you have the base area, you can proceed to determine the total volume. The **volume calculation steps** are straightforward:
- Find the base area using the **triangular area formula**.
- Measure the height of the prism.
- Plug these values into the volume formula: Volume = Base Area × Height.
For example, let’s look at a triangular prism where the base area is already calculated to be 12 cm² and the height of the prism is 10 cm. The total volume would be calculated as follows:
Volume = 12 cm² × 10 cm = 120 cm³
This systematic approach not only clarifies how to calculate volume but also solidifies your understanding of basic geometry involving prisms.
Properties and Real-Life Applications of Triangular Prisms
Understanding **triangular prisms** involves appreciating their **properties** and **applications**. They can be found in nature and various practical settings. For example, the structure of a roof, some architectural designs, or even solid shapes used in packaging. These examples illustrate the relevance of finding the volume of any triangular prism in real-world contexts.
Importance of Triangular Prism Volume in Design
The **importance of triangular prism volume** in design concepts cannot be overstated. In architecture and engineering, calculating the **triangular prism dimensions** correctly ensures that structures are not only aesthetically pleasing but also stable and functional. An accurate understanding of volume helps ensure that materials can be properly assessed for building projects and that weight is distributed evenly across structures.
Visualizing Triangular Prisms in Everyday Life
To fully grasp the properties of triangular prisms, **visualizing triangular prisms** in real life can be quite insightful. For example, consider a glass prism used in light refraction. Understanding its volume is essential for scientists and educators to analyze how light behaves as it passes through various materials.
Moreover, **examples of triangular prisms** can be seen in various shapes like the pyramids in ancient architecture or even simple everyday objects. Observing and measuring these can enrich one’s understanding of geometric principles and volume calculation. This visualization aids in understanding the significance of geometric shapes and their applications in science and design.
Challenges in Computing Volume
While calculating the **volume of a triangular prism** is usually straightforward, challenges can arise, especially in context to measurement units or scaling values. The transition between **volume measurement units** can create confusion, prompting users to familiarize themselves with different standards of measurement.
Problem-Solving with Volume Measurements
Effective **problem-solving with prisms** often involves knowing how to apply the volume formulas in various scenarios. For learning, one could solve real-world problems, such as determining how much material is needed to create a triangular prism box or how to fill a triangular prism-shaped pool. Engaging in these practical examples enhances the learning experience and bolsters comprehension of geometry.
Calculating Areas and Volumes for Advancements
Engaging with **calculating areas and volumes** lays the groundwork for advanced topics in mathematics. As students tackle more complex concepts, a firm grasp of basic geometric principles, like the determination of **triangular prism volume**, aids significantly in their educational journey. This foundational knowledge not only supports academic learning but extends to increasingly intricate real-life problem-solving.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the **triangular prism formula** is essential for accurate volume calculation.
- Calculating the **base area** is the first step in determining volume.
- Visualizing the applications of triangular prisms can enhance comprehension.
- Problem-solving in geometry often involves real-world applications of measurements.
- Equipped with volume calculation skills, one can tackle advanced mathematics with confidence.
FAQ
1. What is the formula for the volume of a triangular prism?
The **triangular prism volume formula** can be expressed as: Volume = Base Area × Height. To find the base area, use the triangle area formula: Base Area = 0.5 × Base × Height of Triangle.
2. How do I convert volume measurements?
Converting **volume measurement units** can be done using conversion factors. For example, to convert cubic centimeters to liters, divide the volume in cm³ by 1000, as 1000 cm³ equals 1 liter.
3. What are some real-life examples of triangular prisms?
Examples of triangular prisms in real life include roofs, wedge-shaped tools, some medals, or even bags for harboring triangular shapes. Understanding these shapes in real-life contexts enhances our comprehension of their usefulness.
4. How does the height of a triangular prism affect its volume?
The **height of the triangular prism** directly influences its overall volume. A taller prism will contain more volume compared to a shorter prism with the same base area. Hence, proper measurement is vital for accurate calculations.
5. Can I find triangular prism volume using software?
Yes, various software for **geometric calculations** can assist with computing the volume of triangular prisms. These tools are quite beneficial in educational settings and professional tasks that require precision.