How to Effectively Disable Windows Defender in 2025
Disabling Windows Defender can sometimes be necessary to install certain software or to improve system performance on your device. This guide will outline various methods you can use to disable Windows Defender effectively in 2025. From basic settings to advanced commands, you’ll find the approach that suits your needs best.
Understanding Windows Defender Settings
Before diving into the process of turning off Windows Defender, it’s essential to understand its features and settings. Windows Defender provides unified security against malware and spyware across various components. The inbuilt Windows Security settings interface allows for managing and adjusting windows defender settings, giving users flexibility in protecting their devices while optimizing resource usage. Depending on the version of Windows you are using, these settings might vary slightly. Typically, users can find security settings under the ‘Update & Security’ section in Windows 10 or Windows 11 settings. Ensuring you know where the controls are will make the disabling process much simpler.
How to Turn Off Windows Defender Permanently
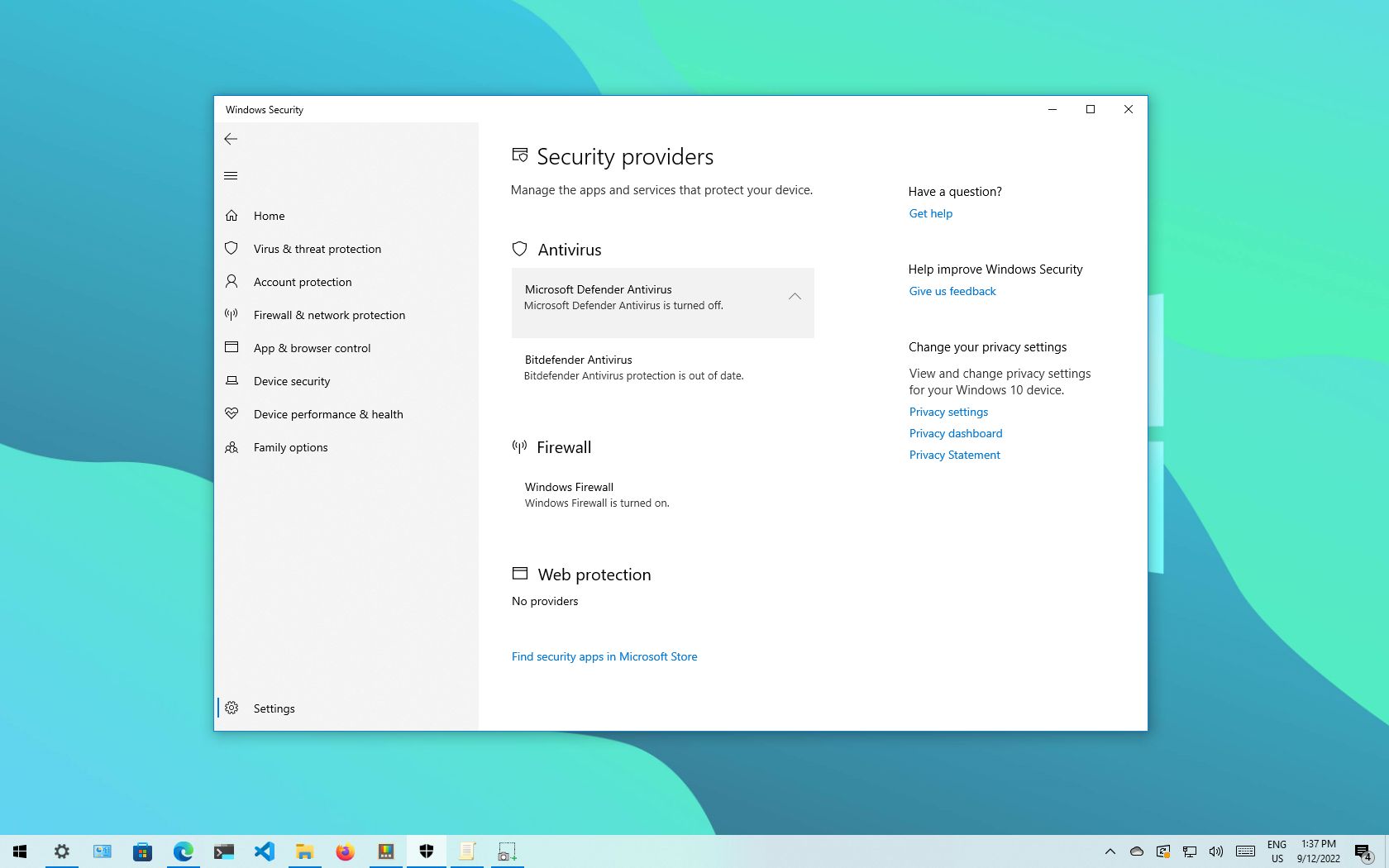
You can permanently turn off Windows Defender by using the system settings. To do this, go to the Start menu, click on Settings, and navigate to Update & Security. Here, select Windows Security, then go to Virus & Threat Protection. Under the ‘Virus & Threat Protection Settings’, you will find a section to disable real-time protection. Toggle the switch to off, and your Windows Defender will be disabled. However, keep in mind that this method requires administrative access, and it’s crucial to have alternative antivirus software installed to keep your device secure.
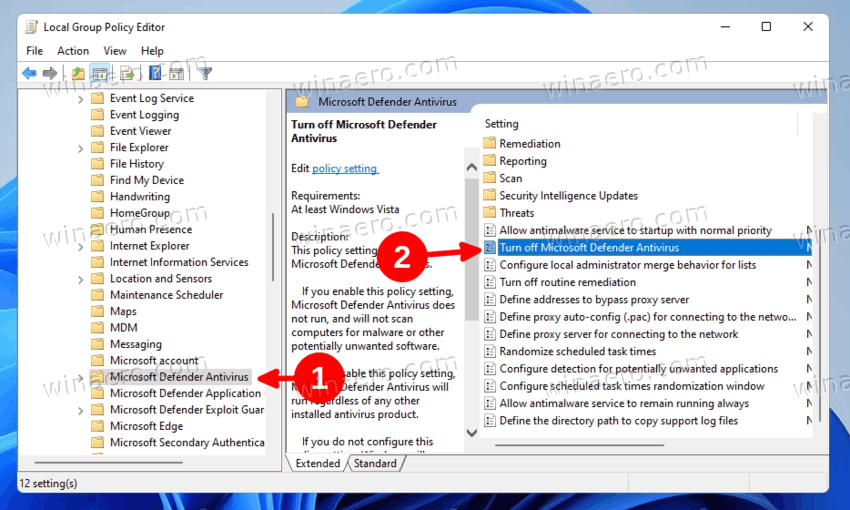
Disabling Defender Through Group Policy
If you are using Windows 10 or 11 Pro and Want a more comprehensive method, the Group Policy Editor provides advanced control over Windows Defender settings. To access the Group Policy Editor, type ‘gpedit.msc’ in the Run dialog (Win + R). Once in the editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Defender Antivirus. In this window, you will find an option to unactivate Windows Defender. Set this policy to ‘Disabled’ to completely turn off Defender. Using Group Policy also ensures that your changes will be retained across system updates and reboots.
Command Line Options to Disable Defender
For tech-savvy users, the command line can be an efficient way to disable Defender. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator and enter the command to disable Windows Defender service. Use PowerShell for more advanced configurations, like disabling Defender’s background scanning. Keep in mind, performing actions through commands alters system settings at a fundamental level, which means it isn’t recommended for those unfamiliar with command-line utilities.
Disabling Windows Defender Temporarily
In some cases, you may only want to disable Defender temporarily. This can be beneficial when installing programs that are falsely flagged as threats. In the Windows Security settings, find the ‘Virus & Threat Protection settings’ and toggle ‘Real-time protection’ off. Remember that this method will automatically reactivate after a certain period or after a system restart, restoring your device protection.
Stopping Defender Automatic Updates
Windows Defender has automatic updates which ensure that your antivirus software remains effective. However, if you’re looking to minimize interruptions, you might want to stop Windows Defender from running during specific periods. This can be managed within the Windows Security settings or by using group policies to control update schedules, ensuring a seamless installation process for other applications without being hindered by constant updates.
Excluding Specific Apps from Defender
If your primary intention is to protect certain applications or processes from Defender’s interference, consider using the ‘Exclusions’ option in the settings. Here, you can add folders or specific applications to stop scans, allowing smoother operation for software that mistakenly triggers Defender. This is particularly helpful when you find that valid applications are unnecessarily flagged or when using third-party software.
Advanced Techniques for Managing Windows Defender
For advanced users, there are several methods to adjust and customize Defender settings, including registry edits and customizing startup behavior of Defender. Utilizing the registry editor, you can modify keys to disable various functionalities of Windows Defender, such as turning off scan schedules or protecting certain software environments. However, these changes should be approached with caution, as incorrect alterations can affect system stability.
Using the Registry Editor for Custom Settings
To disable aspects of Windows Defender via the registry editor, launch the Registry Editor by typing ‘regedit’ in the Run dialog. Navigate to ‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender’. Here, you can create or modify values to control setups like disabling background scans or protection features. It’s crucial to back up the registry before making any changes as mistakes can lead to critical system errors.
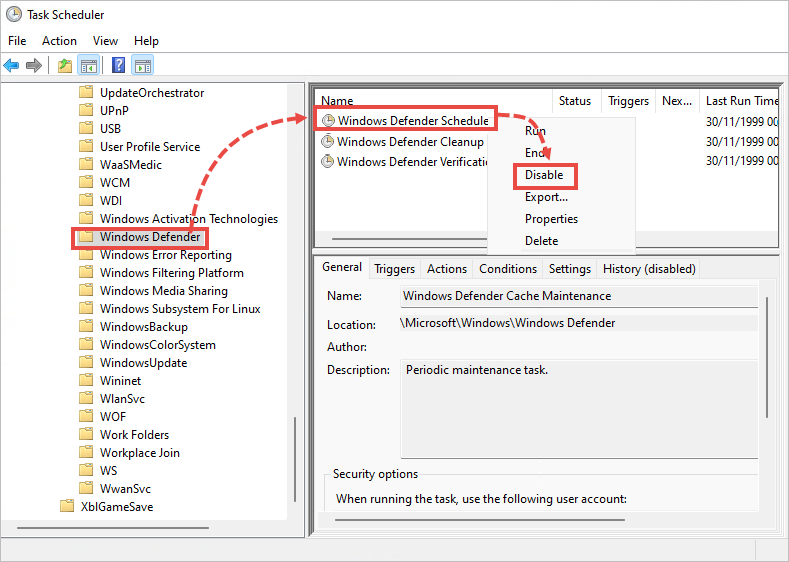
Disabling Defender via Windows Services
Additionally, you have the option to disable the Windows Defender services directly through the services management console. To access this, type ‘services.msc’ in the Run dialog. Find ‘Windows Defender Antivirus Service’ and stop it. Setting the service to ‘Disable’ will prevent it from running on startup, ensuring Windows Defender is effectively turned off each time you boot up your computer.
Summary
Disabling Windows Defender can be an essential step for maintaining system performance and customizing your security setup according to your needs. Whether you choose to do it through settings, group policies, or using command-line tools, understanding the risks and ensuring alternative protections are in place is vital. Keeping the discussion continuous about security measures and best practices will also help in adjusting your approach according to the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
FAQ
1. Can I disable Windows Defender in Windows 11?
Yes, you can disable Windows Defender in Windows 11 using similar methods to Windows 10. By navigating through the Windows Security settings, you can locate options to turn off real-time protection, as well as manage exclusion settings for specific applications.
2. How do I remove Windows Defender from startup?
To remove Windows Defender from startup, you can go into the Windows services management console and set the Windows Defender services to ‘Disabled’. This prevents it from loading automatically when your system starts.
3. Is it safe to turn off Windows Defender when I have third-party antivirus software?
Yes, if you have third-party antivirus software installed and it provides adequate malware protection, it’s generally safe to turn off Windows Defender. Just ensure that the third-party solution is enabled and running correctly.
4. What happens if I disable Windows Defender without another antivirus?
Disabling Windows Defender without another antivirus leaves your system vulnerable to malware and other threats. It is highly recommended to have a protection layer enabled at all times.
5. How can I disable Windows Defender notifications?
You can turn off defender notifications through the Windows Security settings by navigating to the ‘Notifications & actions’ section and disabling options regarding security alerts.
6. What command should I use to disable Windows Defender via Command Prompt?
To disable Windows Defender through Command Prompt, run the command sc stop WinDefend to stop the service. For a more effective method, consider using PowerShell commands for fool-proof disabling.
7. How do I disable sample submission in Windows Defender?
In Windows Security settings, navigate to ‘Virus & threat protection settings’ and find the option to disable ‘Send samples automatically to Microsoft’. This will prevent automatic sample submissions while enabling you to keep more control over what is sent.